The Goods and Services Tax (GST) framework requires businesses to adhere to various compliance mandates, including the filing of annual returns through GSTR-9 and GSTR-9C. Despite their overlapping purposes, these forms serve distinct roles. This guide unravels the key differences between GSTR-9 and GSTR-9C, helping entrepreneurs and professionals make informed decisions while staying GST-compliant.
What is GSTR-9?
GSTR-9 is an annual return consolidating all GST returns filed during a financial year. It provides a comprehensive summary of a taxpayer’s business activities, including turnover, input tax credit (ITC), and taxes paid.
Key Highlights of GSTR-9
Nature: Informational and consolidative.
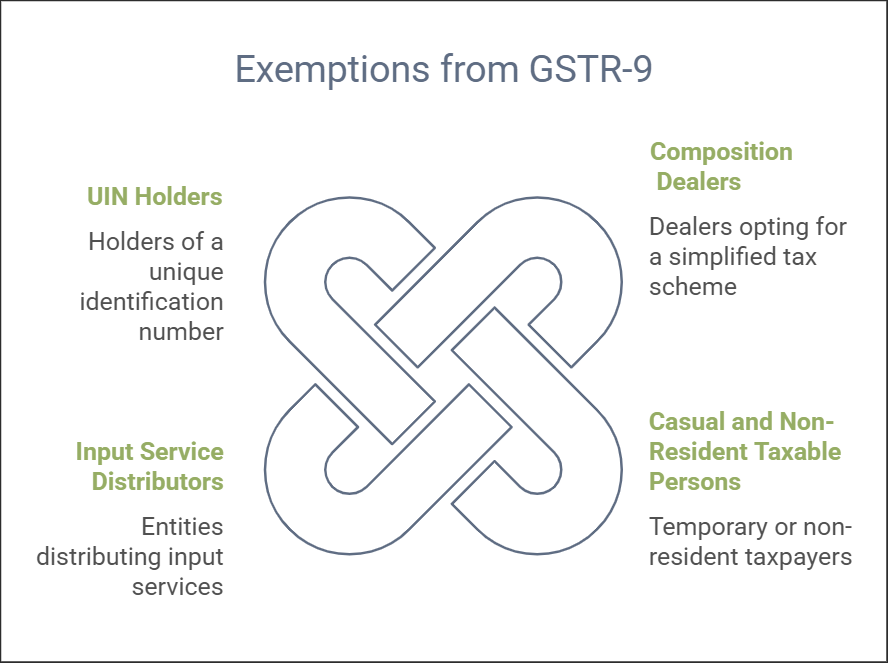
Applicability: Mandatory for all GST-registered taxpayers, except:
Filing Deadline: December 31 of the subsequent financial year.
Penalty for Late Filing: Based on turnover, ranging from Rs 50 to Rs 200 per day of delay.
What is GSTR-9C?
GSTR-9C is a reconciliation statement that matches the data filed in GSTR-9 with the company’s financial records. It includes an auditor’s certification, highlighting discrepancies and potential tax liabilities.
Key Highlights of GSTR-9C
Nature: Analytical, requiring certification.
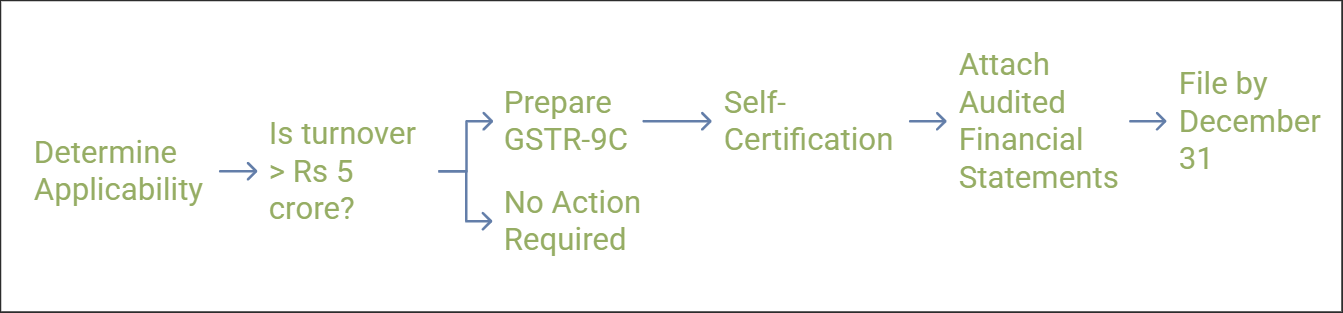
Applicability: Required for businesses with turnover exceeding Rs 5 crore.
Filing Deadline: December 31 of the subsequent financial year, filed with or after GSTR-9.
Certification: Requires self-certification by the CFO or a finance head using a digital signature.
Annexures: Audited financial statements must be attached.
Core Differences Between – GSTR-9 and GSTR-9C
Purpose
- GSTR-9 serves as an annual return that consolidates the taxpayer’s yearly GST transactions, providing a summary of turnover, input tax credit, taxes paid, and any amendments made during the financial year.
- GSTR-9C, on the other hand, is a reconciliation statement that compares the data reported in GSTR-9 with the company’s audited financial statements. It aims to identify discrepancies and determine additional tax liabilities, if any.

Certification Requirement
- GSTR-9 does not require certification by a Chartered Accountant (CA) or Cost Management Accountant (CMA). However, it must be attested by the taxpayer using a digital signature.
- GSTR-9C requires self-certification by the company’s CFO or finance head. Additionally, it includes a reconciliation report and a certification section that must be signed digitally.
Applicability and Turnover Threshold
- GSTR-9 is mandatory for all GST-registered taxpayers except for composition dealers, casual and non-resident taxable persons, input service distributors, and others exempted by law.
- GSTR-9C is required only for businesses with an aggregate annual turnover exceeding ₹5 crore in a financial year.
Details Included
- GSTR-9 contains a consolidated summary of outward and inward supplies, input tax credit claimed, tax paid, amendments, and other relevant details filed during the year.
- GSTR-9C includes a detailed reconciliation between audited financial records and the returns filed, along with recommendations from the auditor regarding any tax discrepancies.
Annexures and Supporting Documents
- GSTR-9 does not require the submission of any annexures or additional documents.
- GSTR-9C mandates the attachment of audited financial statements and other relevant financial records as part of the filing process.

Filing and Penalties
- Both forms have the same deadline — December 31 of the following financial year. However, GSTR-9C can be filed either along with or after GSTR-9.
- GSTR-9 has specific late fee provisions based on turnover, while GSTR-9C attracts general penalties under GST laws if not filed correctly or on time.
By understanding these differences, businesses can better navigate their GST compliance responsibilities, ensuring smooth operations and avoiding unnecessary scrutiny.
Avoiding GST Scrutiny – A CFO’s Perspective
CFOs must focus on robust tax audit processes, meticulous income tax filing, and proper reconciliation of GST returns to ensure compliance. Tools that integrate with GST systems can streamline these tasks, minimizing errors and risks.
Why Choose JD Shah Associates?
JD Shah Associates brings expert guidance for rera registration, Ind AS implementation, and seamless GST return filing. With personalized GST advisory and technology-backed solutions, we simplify tax compliance for businesses of all sizes.
![]()




